Table of contents
- Step 1: Create terraform.tf file
- Step 2: Create provider.tf file
- Step 3: Create a backend.tf file which is for remote backend
- Step 3: Create a main.tf file
- Step 4: Create a my_app_infra_module folder in the same directory.
- Step 5: create my_server.tf this same folder
- Step 6: create my_table.tf this same folder
- Step 7: Create variable.tf this same folder
- Step 8: After all this run these commands
- Conclusion
Hello everyone, I have made a project of terraform in which added terraform.tfstate in remote backend. Additionally, I defined environment-specific configurations, allowing for easy provisioning of infrastructure in multiple environments, such as development, staging, and production. This helped streamline the deployment process and maintain consistency across different environments. And also specifically, I created modules for AWS automations, including the creation of S3 buckets, DynamoDB tables, and EC2 instances. By encapsulating these resources into reusable modules, I achieved a more structured and scalable approach to managing infrastructure.
Please check my repository for the code click here
Step 1: Create terraform.tf file
add these codes in it
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "4.67.0"
}
}
backend "s3" {
bucket = "terraform-gurucharanshettigar-state-s3-bucket"
key = "terraform.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
dynamodb_table = "terraform-gurucharanshettigar-state-dynamoDB-table"
}
}
Step 2: Create provider.tf file
add these codes in it
provider "aws" {
region = var.region
}
Step 3: Create a backend.tf file which is for remote backend
add these codes in it
# backend variable
variable "region" {
default = "us-east-1"
}
variable "s3_state_bucket_name" {
default = "terraform-gurucharanshettigar-state-s3-bucket"
}
variable "dynamoDB_state_table_name" {
default = "terraform-gurucharanshettigar-state-dynamoDB-table"
}
# backend resources
resource "aws_dynamodb_table" "backend_state_s3_bucket" {
name = var.dynamoDB_state_table_name
billing_mode = "PAY_PER_REQUEST"
hash_key = "LockID"
attribute {
name = "LockID"
type = "S"
}
tags = {
Name = var.dynamoDB_state_table_name
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "backend_state_dynamoDB_table" {
bucket = var.s3_state_bucket_name
tags = {
Name = var.s3_state_bucket_name
}
}
Step 3: Create a main.tf file
add these codes in it
# dev
module "dev" {
source = "./my_app_infra_module"
my_env = "dev"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
ami = "ami-007855ac798b5175e"
}
# prd
module "prd" {
source = "./my_app_infra_module"
my_env = "prd"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
ami = "ami-007855ac798b5175e"
}
# stg
module "stg" {
source = "./my_app_infra_module"
my_env = "stg"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
ami = "ami-007855ac798b5175e"
}
here you can see we have defined three environments which is "dev", "stg", "prd"
Step 4: Create a my_app_infra_module folder in the same directory.
create a my_bucket.tf this folder and add thede code in it
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "my_app_s3_bucket" {
bucket = "${var.my_env}-gurucharan-s3-bucket"
tags = {
Name = "${var.my_env}-gurucharan-s3-bucket"
}
}
Step 5: create my_server.tf this same folder
add these code
resource "aws_instance" "my_app_instance" {
count = 2
ami = var.ami
instance_type = var.instance_type
tags = {
Name = "${var.my_env}-instance"
}
}
Step 6: create my_table.tf this same folder
add these code in it
resource "aws_dynamodb_table" "basic-dynamodb-table" {
name = "${var.my_env}-gurucharan-dynamoDB-table"
billing_mode = "PAY_PER_REQUEST"
hash_key = "UserID"
attribute {
name = "UserID"
type = "S"
}
tags = {
Name = "${var.my_env}-gurucharan-dynamoDB-table"
}
}
Step 7: Create variable.tf this same folder
add these code in it
variable "my_env" {
description = "This value of environment"
type = string
}
variable "instance_type" {
description = "This is value of instance type"
type = string
}
variable "ami" {
description = "This is value of ami"
type = string
}
Step 8: After all this run these commands
before running these commands install awscli in system
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
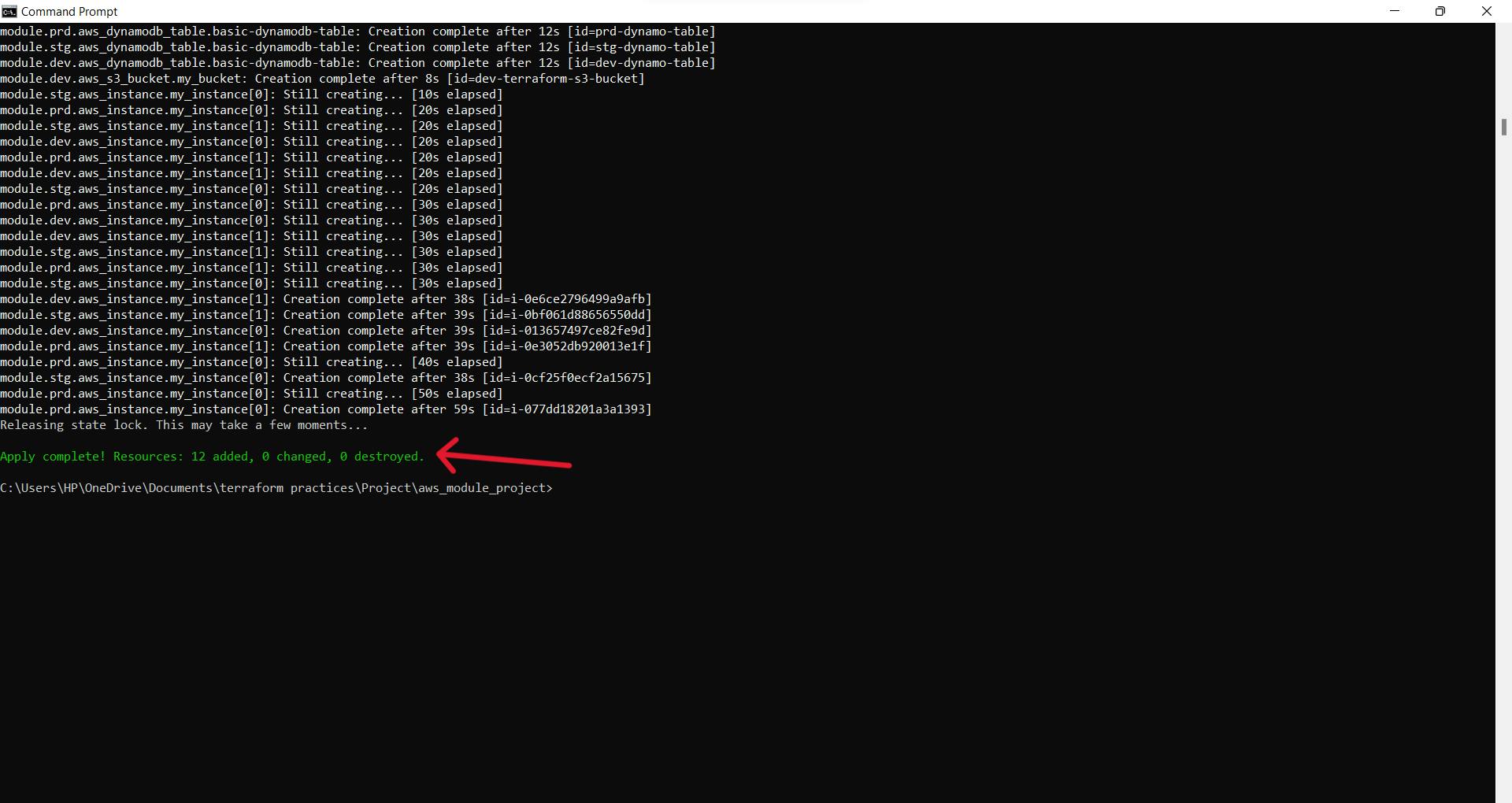
here you can see we have successfully created all the buckets and table
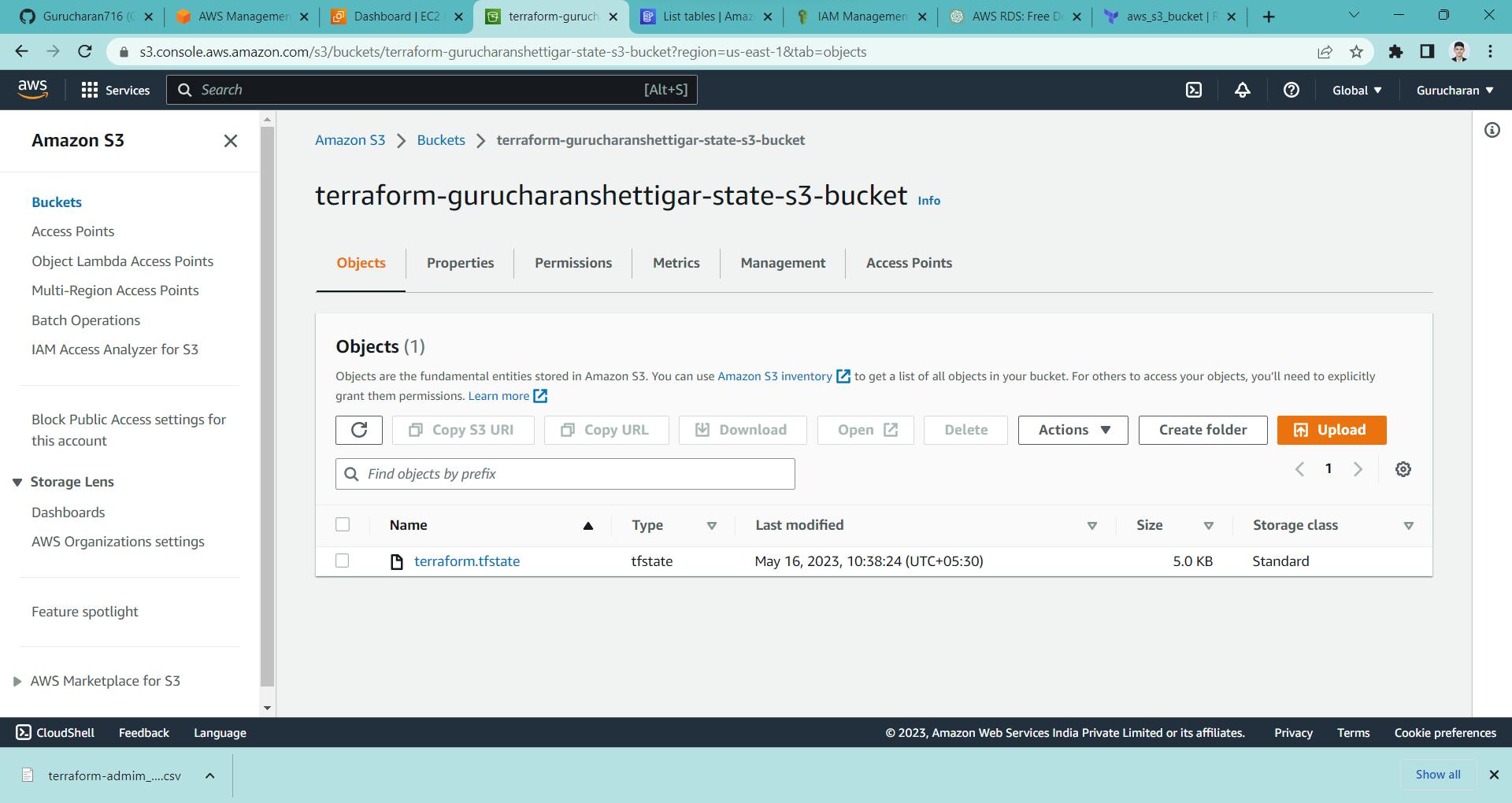
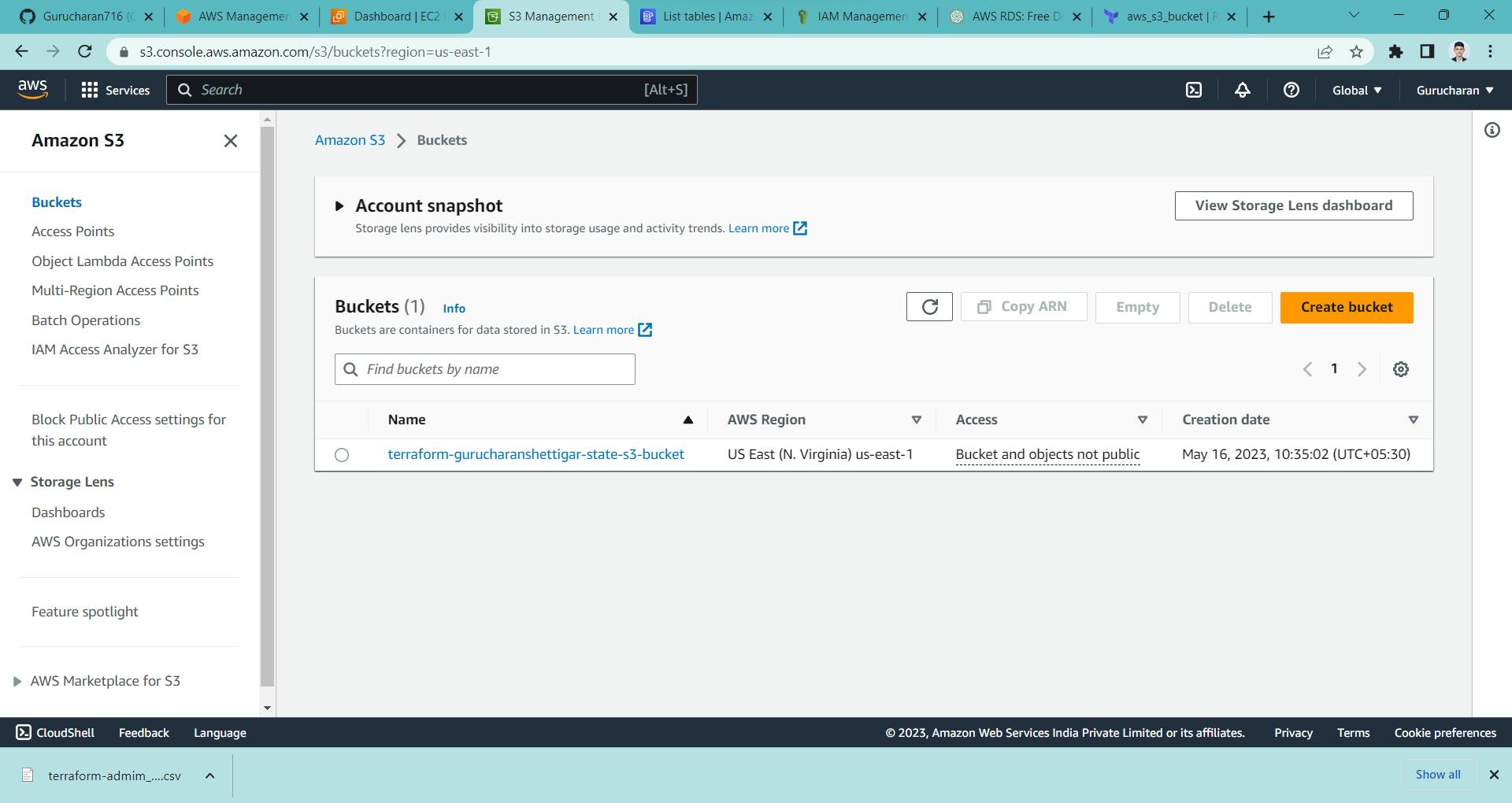
here we have added the remote backend of terraform.tfstate
Here are the images in which we have created AWS s3 bucket, AWS dynamoDB and AWS EC2 instance by terraform
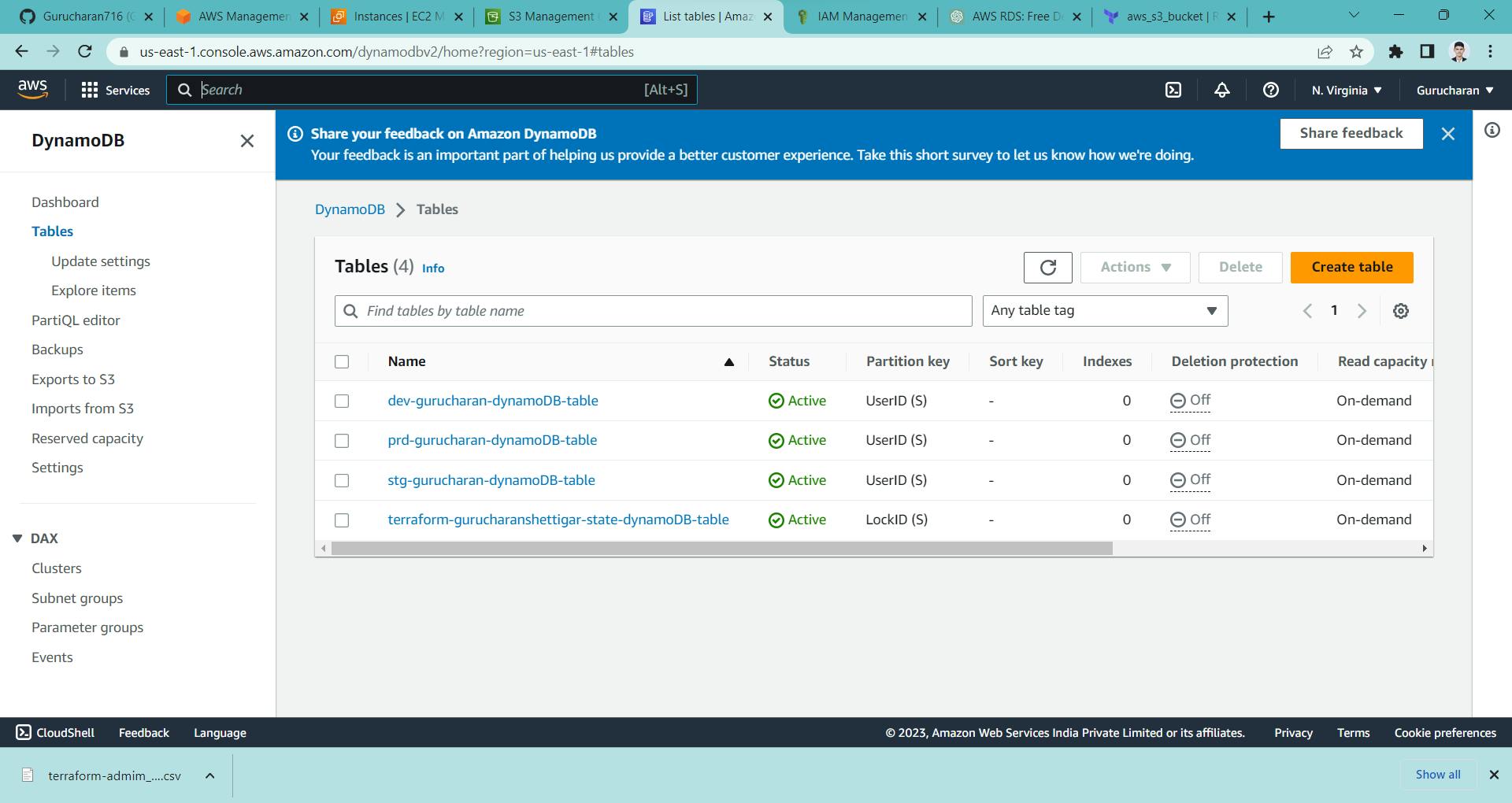

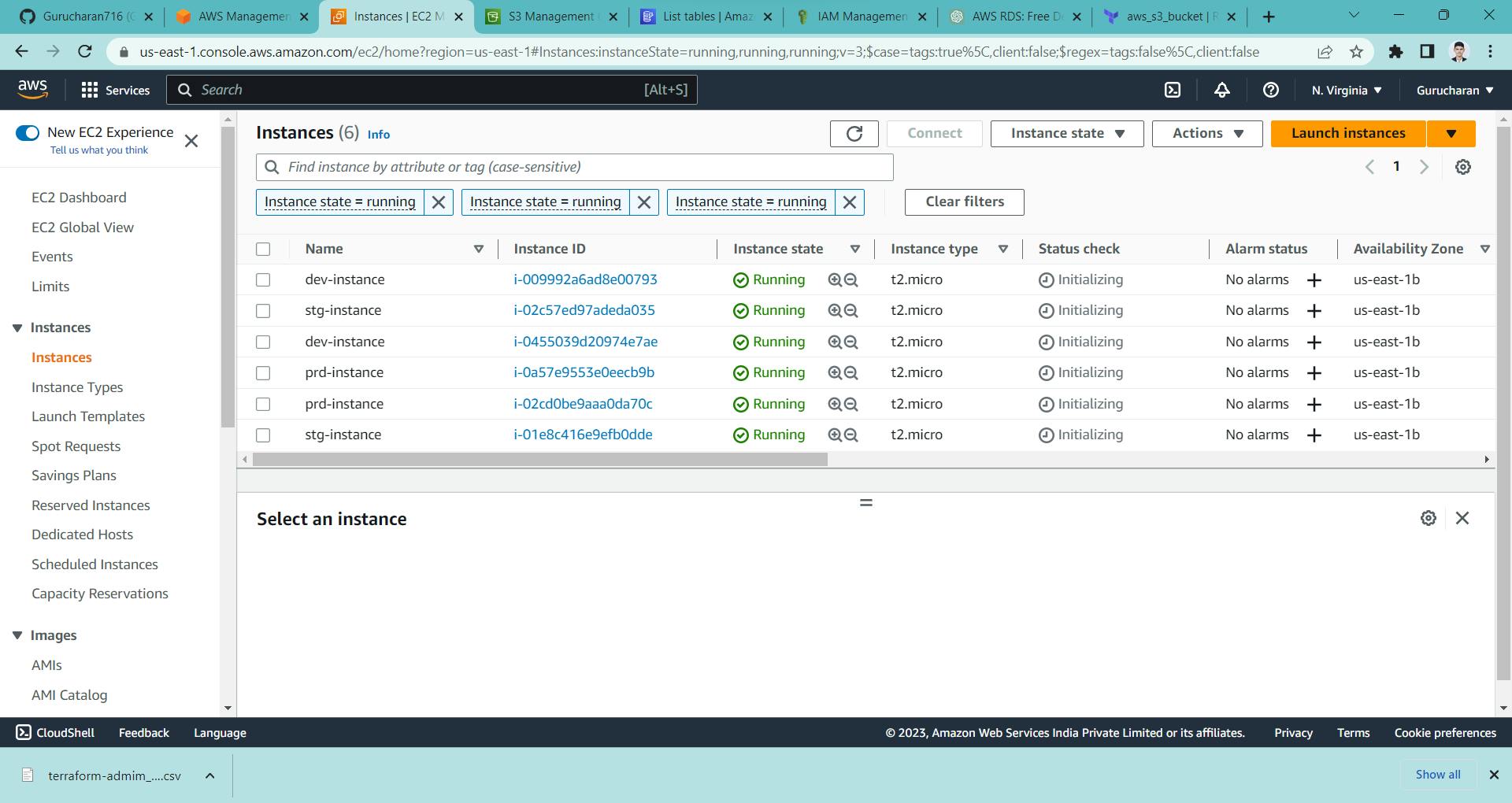
Conclusion
This Terraform project showcased ability to optimize infrastructure management and promote automation through the use of best practices. By implementing a remote backend for storing the terraform.tfstate file, I ensured consistent state management and facilitated collaboration among team members. The inclusion of environment-specific configurations allowed for streamlined deployment across different environments.
Overall, this project highlighted my strong grasp of Terraform and its capabilities in managing cloud infrastructure. By incorporating remote state management, environment configurations, and modularization, I delivered an efficient and scalable solution for infrastructure deployment and management. I am confident that the skills and experiences gained from this project will prove valuable in future endeavors involving infrastructure automation and cloud management.
Thank you for reading this blog and if any queries or if any corrections to be done in this blog please let me know.
contact us in Linkedin ,Twitter or email-id gurucharanu716@gmail.com